Definition of Cryogenics
Cryogenics is the study of extremely low temperatures and of how those materials behave when they get there. The cryogenic temperature range has been defined as from -150 degrees, Celsius to -273 degrees Celsius, or absolute zero. Cryogenic temperatures are usually described in the absolute or Kelvin temperature scale, in which absolute zero is written as 0K, without a degree sign. The temperature at which molecular motion comes to a stop is theoretically possible to ceasing completely. This leads to the next topic, the Kelvin scale.
Kelvin Scale
At very low temperatures, molecules come to a complete halt and behave very differently than when they were in a warmer state. These temperatures are written out in the Kelvin scale, as opposed to the regular degrees. It is especially designed to have the temperature at which atoms stop moving be 0K. Therefore the concept of absolute zero is easier to calculate and comprehend. The conversion equation from Celsius to Kelvin is to just add 273 to whatever Celsius equation you have.

Kinetic Molecular Theory
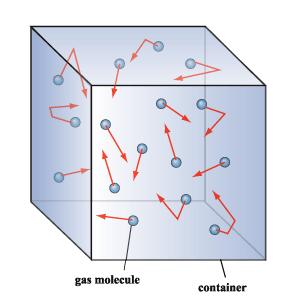
The Kinetic Molecular Theory explains the forces between molecules and the energy that they possess. Matter is composed of small particles (molecules). The measure of space that the molecules occupy (volume) is derived from the space inbetween the molecules and not the space the molecules contain themselves. The following list below is of the five postulates of this theory.
- A gas consists of a collection of small particles traveling in straight-line motion and obeying Newton's Laws.
- The molecules in a gas occupy no volume (that is, they are points).
- Collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic (that is, no energy is gained or lost during the collision).
- There are no attractive or repulsive forces between the molecules.
- The average kinetic energy of a molecule is 3kT/2. (T is the absolute temperature and k is the Boltzmann constant.)
Because cryogenic temperatures do not occur naturally, scientists had to come up with certain methods in order to figure out how exactly that would work. That is, how on earth they could get temperatures so low that the atoms would actually almost stop moving (almost because even after all, they have only gotten about a millionth or so away from that theoretical zero Kelvin temperature.) This theory was instrumental in understanding how to do that. By molecules slowing down, the temperature goes down. By knowing this,
scientists were able to come up with many way in which to cool things down cryogenically
because they knew that by slowing down the particles in a container, it would get colder. By
knowing the certain speed of molecules and their resistance, scientists were able to discover
which molecules were able to cool down so much so that they could make a cryogenic fluid. Examples
of these molecules include liquid Nitrogen, Helium, and Oxygen.



No comments:
Post a Comment